Computer System
A computer system is a set of integrated devices that inputting , processing and outputting the storing data and information is known as computer system.
A computer is a programmable machine, which is designed to perform arithmetic and logical operations automatically and sequentially on the input given by the user and provides the required output after processing.
Computer components are divided into two major categories : hardware and software
computer hardware includes the physcal parts of the computer such as CUP, Memory monitor, keyboard and mouse etc.
Software are the set of programs that instruct the hardware for performing various functions.
Components of a Computer System
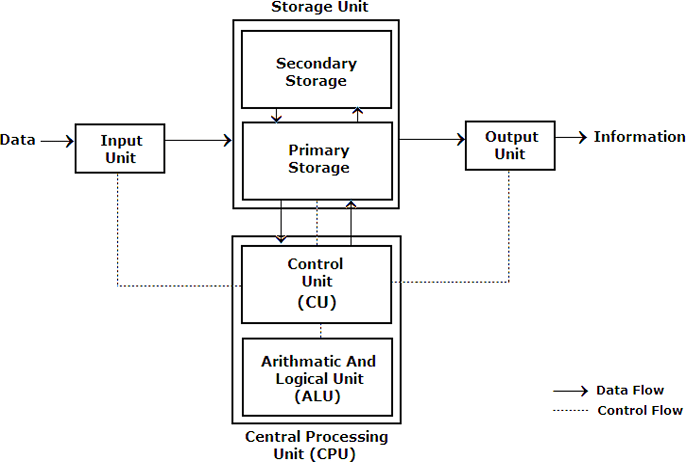
Computer hardware provides the physical mechanisms to process, store, and input /output data. Includes CPU, memory, I/O devices.
Software provides instructions to tell the hardware what tasks to perform. It includes system and application softwares.
Data in the computer may be representing numbers, characters, graphics etc but is always kept in a form that the hardware and software can understand and manipulate.
Input Unit
• Computer receives data and instructions through the Input Unit.
• The input unit consists of one or more input devices.
• Input devices include:
- Keyboard
- Mouse
- Joystick
- Scanner
Function of Input Unit
- Accept the data and instructions from the outside world.
- Convert it to a form that the computer can understand.
- Supply the converted data to the computer system for further processing.
Output Unit
• Computer provides information and results of computation to the outside world through the Output Unit.
• The output unit consists of one or more output devices.
• Output devices include:
- Monitor
- Printer
- Speaker
Function of Output Unit
- Accept the results produced by the computer. (These are in a coded form.)
- Convert it to a form that the outside world can understand. (OR, Converts it into human readable form.)
- Supply the converted results to the outside world.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
CUP is the brain of the computer
The ALU and the Control Unit (CU) of a computer system are jointly known as the central processing unit.
CUP= CU+ALU
CPU performs actual processing of data, according to instructions from programs
Parts of the CPU
- CONTROL UNIT (CU)
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
- Registers
Functions of CUP
- It performs all calculations.
- It takes all decisions.
- It controls all units of the computer
Control Unit
• It controls all other units in the computer.
• It is the central nervous system of the computer that controls and synchronizes its working.
Functions of Control Unit
- controls data movement and execution of instructions(when to receive , where to store and when to display)
- It instructs the input unit, where to store the data after receiving it from the user and
- It controls the flow of data and instructions from the storage unit to ALU.
- It also controls the flow of results from the ALU to the storage unit.
- The control unit determines the sequence in which computer programs and instructions are executed.
- The control unit is also capable of shutting down the computer when the power supply detects abnormal conditions.
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
All calculations are performed in the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) of the computer.
•Whenever calculations are required, the control unit transfers the data from memory to ALU. Once the computations are done, the results are transferred to the memory by the control unit and then it is send to the output unit for displaying results.
Arithmetic Operations
- Addition
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Division
Logical Operation
- AND
- OR
- IF
- ELSE
- Greater Than (>)
- Leass Than (>)
- Greater Than or Equal (>=)
- Less Than or Equal (<=)
- Equal (=)
- Not Equal (!=)
Function of Arithmetic Unit
- It performs all arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division).
- It performs all logic operations (Logic operations test various conditions encountered during processing and allow for different actions to be taken based on the results. )
- It does comparison and takes decision.
Registers
Registers are small high speed storage areas.
They hold various type of data, instruction, Address and the immediate result of the calculations when AlU performs arithmetic and logical operation
To execute an instruction the control unit of the CPU retrieves it from main memory and place it into a register
Registers Type
- Program counter
- Memory address Register
- Instruction Register
- Memory buffer register
- Memory data register
- Accumulator
Program Counter(PC)
•To keep the track of the next instruction to be executed.
Instruction Register(IR)
•To hold instruction to be decoded by the control unit
Memory Address Register(MAR)
•To hold the address of the next location in the memory to be accessed
Memory Buffer Register(MBR)
•For storing data received from or sent to the CPU.
Memory Data Register(MDR)
•For storing operands and data
Accumulator(ACC)
•For storing the results produced by arithmetic and logic units.
Storage Unit
The storage unit of the computer holds data and instructions(either temporarily or permanently) that are entered through the input unit, before they are processed
Function of Storage Unit
- It received the data and instructions required for processing from the input unit.
- It stores the intermediate results.
- It stores the final results before these results are released to the output unit.
- It saves data for later use.
Type of Memory
- Primary Memory
- Secondary Memory
Read More : Hierarchy of Memory