Memory hierarchy refers to the organization and arrangement of different types of memory in a computer system, based on their speed, capacity, and cost.
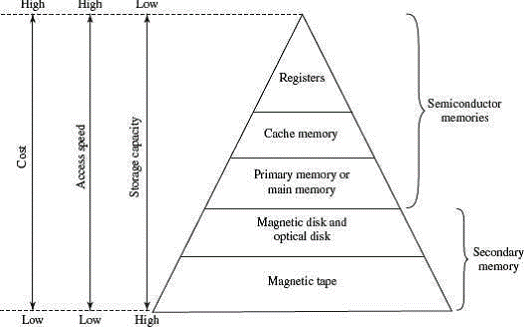
The memory at the top of the hierarchy has high speed, less storage, and is the most expensive. As you move down the hierarchy, speed and cost decrease, while storage increases.
Type of Memory
Primary memory
Primary memory stores data and programs while the program is being executed.
Primary memory is also known as main memory
Primary memory devices are volatile i.e its content is totally removed when power is switch off.
Example : Cache Memory RAM, ROM, cache
Secondary memory
The secondary memory stores data and programs for long periods of time. It provides large, non-volatile and cheap storage for programs and data
example:
Example : Magnetic tape, magnetic disk ,Hard disk, floppy disk.
Difference between primary and Secondary Memory
| ON the Basis of | Primary Memory | Secondary Memory |
| Nature | Volatile | Non-volatile |
| Storage capacity | Small | Large |
| memory | Semiconductor | Magnetic and optical memory |
| speed | Fast | Slow |
| cost | High cost | Low cost |
| Memory Hierarchy | Higher position | Lower position |
| example | RAM, ROM Cache | Magnetic tape, magnetic disk ,Hard disk, floppy disk |
Cache Memory
Cache memory is similar to RAM, except that it is extremely fast compared to normal memory and it is used in different way.
Cache memory is a small memory that resides between CPU and RAM whose access time is closer to the processing speed of the CPU.
When program is running and the CPU needs to read data and program instruction from RAM, the CPU check first to see whether the data is in cache memory. If the data is not there the CPU read the data from RAM into its register , but it also loads a copy of data into cache memory.
The next time the CPU needs that same data , it finds it in the cache memory and saved the time needed to load the data from RAM.
The successful retrieval of requested data from the cache is known as cache hit.
Failure to find the requested data in the cache is known as cache miss.
Type of cache memory:
Primary cache (level 1/ internal cache)
• It is located inside the CPU.
• It is smaller and fastest
Secondary cache (level 2/ external cache )
• It is located outside the CPU; normally positioned on the motherboard of a computer.
• It is larger but slower than primary cache
Registers
Registers are small high speed storage areas.
They hold various type of data, instruction, Address and the immediate result of the calculations when AlU performs arithmetic and logical operation
To execute an instruction the control unit of the CPU retrieves it from main memory and place it into a register.
Registers Type
- Program counter
- Memory address Register
- Instruction Register
- Memory buffer register
- Memory data register
- Accumulator
