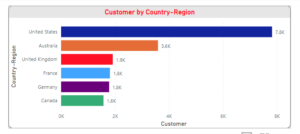
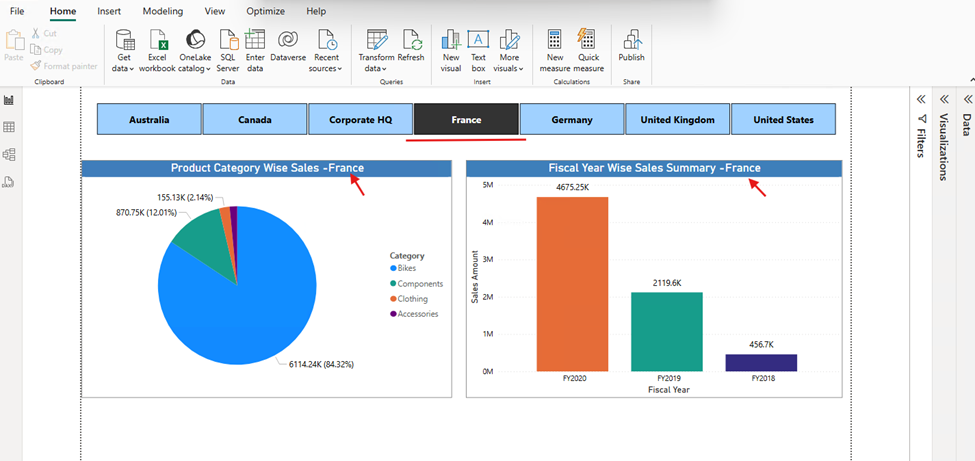
In today’s data-driven world, making sense of information quickly and accurately is essential for business success. Two of the most widely used tools for data analysis are Microsoft Excel and Power BI. While both are developed by Microsoft and offer strong data capabilities, they are designed for different types of tasks.
Here’s a simple guide to help you understand when to use Excel, when to use Power BI, and how both can work together.

Excel: Best for Custom, Quick Analysis
Excel is a long-time favorite for professionals. It’s flexible, easy to use, and great for day-to-day data tasks.
Use Excel When:
- You’re working with small or medium-sized datasets
- You need quick calculations or models
- You’re building reports or financial templates
- You need custom formulas and flexible layouts
- Reports are for internal or individual use
Excel Strengths:
- High control over formulas and logic
- Great for budgeting and financial models
- Fast setup for ad hoc reports
- Familiar to most business users
Excel Limitations:
- Manual data updates
- Hard to manage across large teams
- Error-prone in complex setups
- Limited in live data connection and interactivity
Power BI: Ideal for Scalable, Real-Time Insights
Power BI is a modern tool for creating interactive dashboards and reports. It’s designed for organizations that need to manage large data and share insights across teams.
Use Power BI When:
- You deal with large or multiple data sources
- You need dashboards that update automatically
- You want to share reports across departments
- You need user-level data security and access control
- Your reports require interactive visuals
Power BI Strengths:
- Connects to over 100 data sources
- Real-time data refresh and automation
- Easy to share dashboards
- Strong data modeling and filtering tools
- Better for team collaboration and governance
Power BI Limitations:
- Not ideal for quick one-off analysis
- Requires setup and data modeling
- May need technical knowledge for advanced features
- Learning curve for new users
Excel + Power BI: Better Together
Rather than choosing one over the other, many businesses benefit from using both Excel and Power BI together:
- Power BI can connect to Excel files as data sources
- Excel can analyze data from Power BI datasets
- Use Excel for building models, and Power BI to share results
- Power BI ensures data control and visibility, while Excel supports deep analysis
Which Tool Should You Use?
Here’s a quick decision table:
| Use Case | Recommended Tool |
|---|---|
| One-time or quick analysis | Excel |
| Budgeting and financial modeling | Excel |
| Real-time dashboards | Power BI |
| Reports across multiple departments | Power BI |
| Data visualization for clients | Power BI |
| Complex financial logic | Excel |
| Working with live data from sources | Power BI |
Conclusion
Choosing between Excel and Power BI depends on your goals, the complexity of your data, and how the information will be used. In many cases, the best approach is to use both tools together to get the best of both worlds.
At Reboot Software, we can help you build the right strategy using Excel, Power BI, or a combination tailored to your business needs.
For more about Power BI