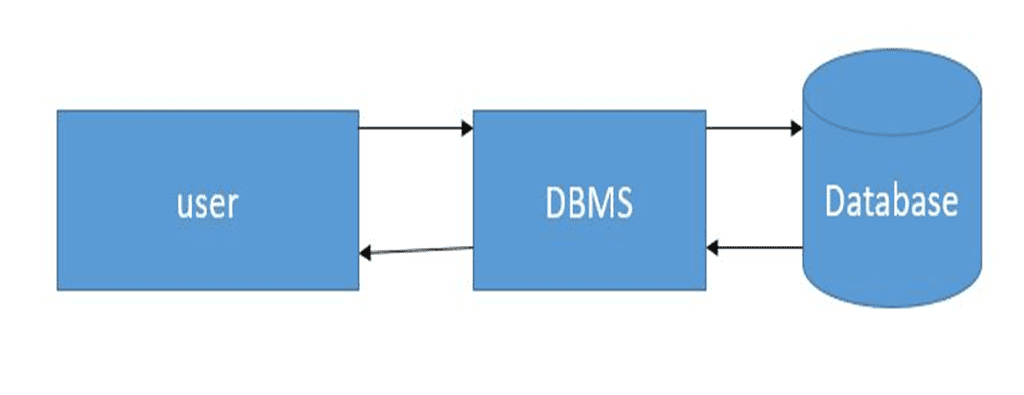
Database management system (DBMS) is a type of software or tools that helps to manage the database. User can create , maintain, manipulate and retrieve data or information from a single table or group of interrelated table.
DBMS act as an interface between user/application program and database.
Example : Oracle Database , SQL Server, MySQL, MS-access, Dbase etc. are used to managed data in DBMS.
DBMS application are Student information system, hospital management system ,Library Management System, customer relationship Management.
Major role of DBMS
- Define data structure for data storage
- Provide suitable mechanism for data access and data manipulation.
- Maintain system integrity.
- Eliminates redundancy of data
- Provide safety and security measure of data.
- Provide mechanism for data sharing among user concurrently
Advantage of DBMS
- Make an easy to view data, add new data, modify and delete existing data.
- Organize the data in proper sequence and Structure.
- Eliminates data redundancy ( Same data set is stored in multiple places)
- Data consistency (Data consistency is the accuracy, completeness, and correctness of data stored in a database)
- Data can be shared among several users.
- Protecting data against unauthorized access.
- Allow for multiple user to be active at one time ( Data can be accessed concurrently)
- Data Backup and Recovery.
Disadvantage of DBMS
- Cost of Hardware and Software of a DBMS is quite high, which increases the budget of your organization.
- Most database management systems are often complex systems, so the training for users to use the DBMS is required.
- The database can fail because or power failure or the whole system stops.
- Chances of unauthorized access (security risk)
- Need more disk space for program storage then file management system.
Objectives of the DBMS
- To store mass storage of relevant data.
- To Make the data access easy for the user.
- To eliminate the data redundancy.
- To Make the latest modification to the database available immediately
- Allow for multiple user to be active at one time ( Data can be accessed concurrently)
- The advancement in the database enables to add more data and program to the system
- To Protect the data from physical harm and unauthorized access.
- To Maintain Data confidentiality.
Read also: Introduction to Database