Introduction to Data Engineering
Data engineering is the backbone of modern data-driven businesses, focusing on building systems to collect, store, and analyze vast amounts of data. It encompasses everything from designing data pipelines to ensuring data is clean, secure, and accessible for analytics and decision-making. As companies increasingly rely on data to drive innovation, data engineering has become one of the most critical and in-demand fields in the tech industry.
The Scope of Data Engineering
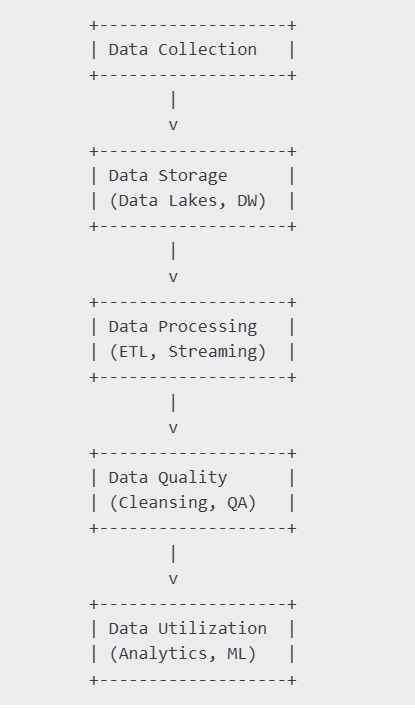
The scope of data engineering spans multiple critical areas, including data collection, storage, processing, quality, and utilization. It enables businesses to handle large-scale data efficiently while ensuring it is ready for analysis and decision-making. Data engineers play a pivotal role in building robust data pipelines, maintaining data governance, and supporting advanced analytics and machine learning initiatives. As technology evolves, data engineering continues to expand its impact across industries.
Below is a visual representation of the evolving scope of data engineering:
Top Questions and Trending Topics in Data Engineering
1. What does a data engineer do?
Data engineers are responsible for designing, building, and maintaining systems that allow organizations to collect, store, and analyze large amounts of data. They ensure that data pipelines are efficient, scalable, and reliable. Their tasks often include:
- Developing ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes.
- Managing data storage solutions like data warehouses or data lakes.
- Ensuring data quality and security.
- Collaborating with data analysts and data scientists to provide them with clean, well-structured datasets.
2. Is data engineering a lot of coding?
Yes, data engineering involves a significant amount of coding. Data engineers use programming languages like Python, Java, Scala, and SQL to create and maintain data pipelines, automate workflows, and manage data integration processes. While coding is essential, the level of coding required can vary depending on the organization and the specific tools they use.
3. Are data engineers highly paid?
Yes, data engineers are among the top earners in the tech industry due to the critical role they play in handling and processing big data. Salaries vary depending on location, experience, and industry, but the demand for skilled data engineers ensures competitive compensation packages. In addition, proficiency in cloud platforms, big data tools, and programming languages can significantly boost earning potential.
4. Is data engineering just ETL?
No, data engineering goes far beyond ETL. While ETL processes are a key part of the role, data engineers are also involved in:
- Designing and maintaining data architectures.
- Optimizing query performance.
- Implementing data governance and security measures.
- Building scalable data pipelines to support machine learning models and real-time analytics. The field has evolved significantly with advancements in cloud computing, real-time streaming, and distributed systems.
Trending Topics in Data Engineering
1. What is the latest in data engineering?
Recent advancements in data engineering include:
- The rise of DataOps to streamline and automate data pipeline development.
- Adoption of lakehouse architecture, which combines the benefits of data lakes and data warehouses.
- Increased use of streaming platforms like Apache Kafka for real-time data processing.
- Integration of AI and machine learning to optimize data workflows and quality checks.
2. What’s next for data engineering in 2024?
The field of data engineering is expected to focus on:
- Serverless technologies to reduce infrastructure management overhead.
- Enhanced emphasis on data governance and compliance due to evolving regulations.
- Growth in real-time analytics, fueled by IoT and edge computing.
- Increased adoption of data mesh principles, promoting decentralized data ownership.
3. What are the 4 V’s of data engineering?
The 4 V’s represent the challenges and characteristics of handling big data:
- Volume: Managing the sheer scale of data being generated.
- Velocity: Processing data at high speed to enable real-time analytics.
- Variety: Integrating diverse data formats and sources.
- Veracity: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data.
4. What is the future of data engineering?
The future of data engineering will likely emphasize:
- Greater adoption of cloud-native architectures.
- Evolution of low-code and no-code data tools to democratize data access.
- Increased collaboration between data engineers and other roles like data scientists through unified platforms.
- Expanded focus on ethical data practices and sustainability in data processing.
online Courses for Free with Certificate
Free online course with certificate : Click here
Practice Question: Click Here
Read More:
What is Data engineering in Microsoft Fabric?
Microsoft Certified: Fabric Data Engineer Associate