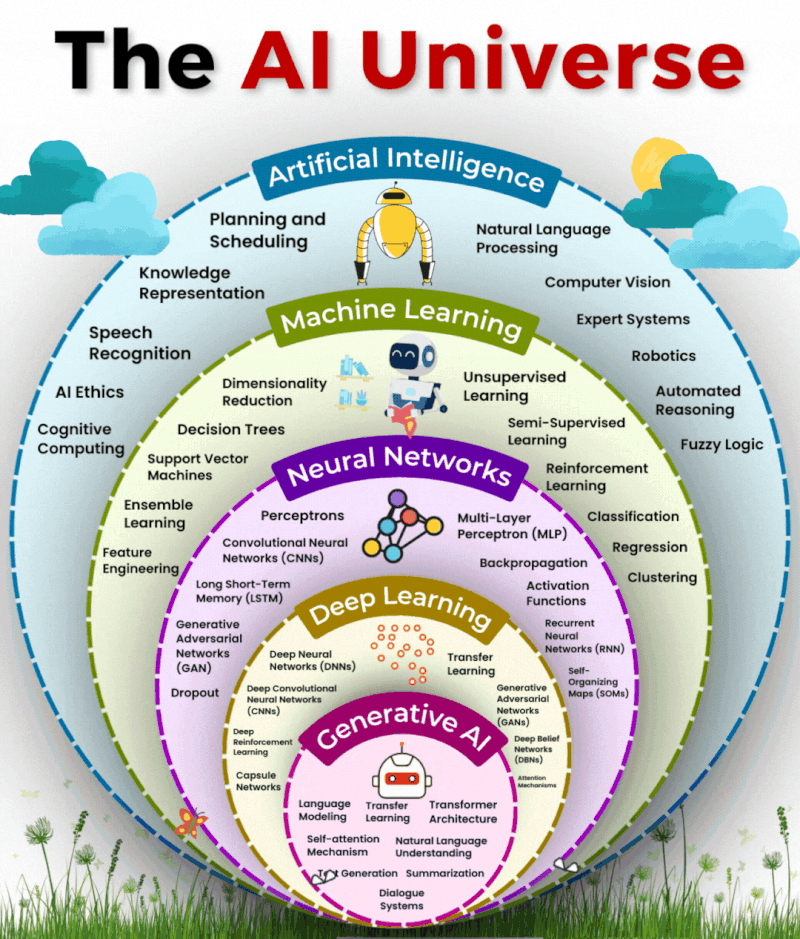
The AI Universe
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly evolved from a futuristic concept to a core part of our everyday lives. From recommending movies and translating languages to generating art and powering robots, AI touches nearly every industry. But AI is not a monolithic technology—it’s a vast universe made up of several powerful domains like Machine Learning (ML), Neural Networks (NN), Deep Learning (DL), and Generative AI (GenAI).
This article breaks down the layers of this AI universe in simple language, so you can understand how it all connects.
1. What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence is the science of building smart machines that can mimic human intelligence—thinking, reasoning, problem-solving, and even creativity.
🔹 Key Applications of AI:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Used in chatbots, language translators, and voice assistants.
- Computer Vision: Enables machines to “see” and interpret visual data like images and videos.
- Planning and Scheduling: Helps in logistics, autonomous vehicles, and smart factories.
- Expert Systems: Software that mimics human decision-making using rules and logic.
- Robotics: AI controls physical machines to perform complex tasks.
- Automated Reasoning and Fuzzy Logic: Useful in uncertain or imprecise situations like weather forecasting or risk analysis.
- AI Ethics and Cognitive Computing: Address moral, ethical, and human-like reasoning challenges.
In short, AI is the brain behind automation and smart decision-making across industries.
2. Machine Learning (ML): The Learning Engine of AI
Machine Learning is a core part of AI where computers learn from data without being explicitly programmed. It powers most modern AI systems by training models on massive datasets.
🔹 Types of Machine Learning:
- Supervised Learning: The model learns using labeled data (e.g., spam detection).
- Unsupervised Learning: The model finds hidden patterns in unlabeled data (e.g., customer segmentation).
- Semi-Supervised Learning: Combines small labeled data with large unlabeled data for training.
- Reinforcement Learning: The model learns by interacting with an environment and receiving rewards or penalties (used in game AI and robotics).
🔹 Popular ML Techniques:
- Decision Trees & Random Forests
- Support Vector Machines (SVM)
- Clustering (like K-Means)
- Dimensionality Reduction (like PCA)
- Ensemble Learning – combining multiple models for better accuracy
ML acts like the learning mechanism of AI—allowing it to improve over time.
3. Neural Networks: AI Inspired by the Brain
Neural Networks are the mathematical structures that power modern AI. Inspired by the human brain, they consist of layers of nodes (neurons) connected together to process data and make predictions.
🔹 Core Concepts:
- Perceptron: The simplest neural unit that mimics a single brain neuron.
- Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP): A network with input, hidden, and output layers.
- Backpropagation: An algorithm to improve model accuracy by adjusting internal weights.
🔹 Types of Neural Networks:
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Best for image recognition and computer vision.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Ideal for sequences—used in text, speech, and time-series data.
- Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM): A type of RNN designed to remember information over long sequences.
Neural networks are the digital “brain cells” that make intelligent tasks like image detection or language translation possible.
4. Deep Learning (DL): Going Deeper Into AI
Deep Learning is a subset of ML that uses very deep neural networks with many layers. These models automatically extract high-level features and are responsible for many breakthroughs in AI today.
🔹 Deep Learning Models:
- Deep Neural Networks (DNNs)
- Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (DCNNs) – used in self-driving cars, facial recognition
- Deep Reinforcement Learning (used in AlphaGo, robotics)
- Dropout and Regularization: Techniques to reduce overfitting and improve generalization
🔹 Transfer Learning:
This allows you to use a pre-trained model on a new task, significantly reducing training time and resources. For example, using a model trained on ImageNet to detect medical anomalies.
Deep Learning is behind many AI marvels—like Google Translate, Netflix recommendations, and autonomous drones.
5. Generative AI (GenAI): Creating Like a Human
Generative AI is the newest and most exciting frontier of the AI universe. Unlike traditional AI that analyzes or classifies data, GenAI creates new content—text, images, code, music, and more.
🔹 Examples:
- ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini: AI that generates human-like text.
- DALL·E, MidJourney: Create realistic images from text prompts.
- Deepfake Generators: Swap faces or voices convincingly.
- Code Generation Tools: Like GitHub Copilot that helps you write code.
🔹 Core Technologies:
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): A “generator” creates content and a “discriminator” critiques it, pushing the model to improve.
- Transformer Architecture: Powers models like GPT and BERT—great for language tasks.
- Self-Attention Mechanism: Allows models to focus on relevant parts of data, making context-aware predictions.
- Language Modeling and Natural Language Understanding (NLU): Enables chatbots, summarizers, and translators.
GenAI is transforming creativity, education, business, and even healthcare. It’s like giving machines the power to imagine.
Conclusion
The AI universe is rapidly expanding. Technologies are evolving at breakneck speed, and what was once science fiction is now shaping our present and future.
From AI planning robots to deep-learning-powered diagnostics, and from GAN-generated art to transformer-based assistants, we are only scratching the surface.
Practice Power BI and Data Science Multiple Choice Questions