The data and artificial intelligence industry offers multiple career paths, each with its own responsibilities, skill sets, and tools. Roles such as Data Analyst, Data Scientist, Machine Learning Engineer, and GenAI Engineer are often confused, yet they serve very different purposes.
This article explains the key differences between these roles to help you choose the right career path based on your interests and goals.
Understanding the Data and AI Career Ecosystem
Data-driven organizations rely on a sequence of roles that transform raw data into insights, predictions, and intelligent systems. These roles range from analysis and decision-making to engineering and AI deployment.
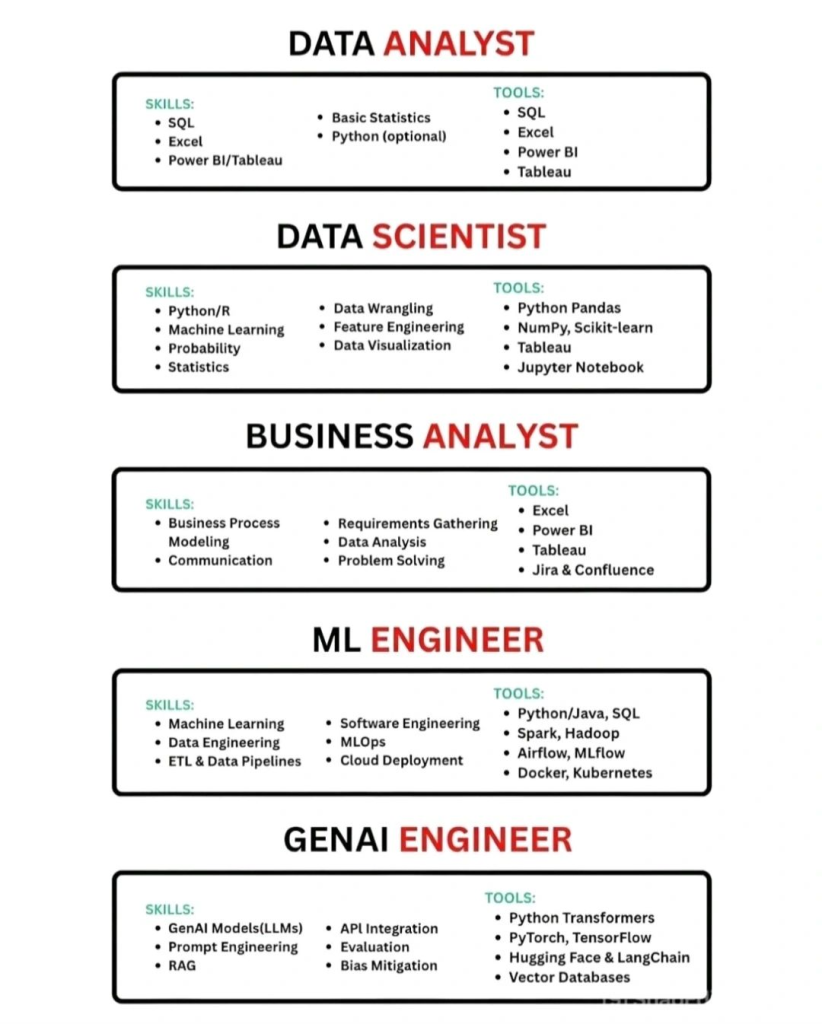
Data Analyst
Role Overview
A Data Analyst focuses on analyzing historical and current data to identify trends, patterns, and performance metrics. Their work supports business decision-making through reports and dashboards.
Core Skills
- SQL
- Excel
- Power BI or Tableau
- Basic statistics
- Python (optional)
Common Tools
SQL, Excel, Power BI, Tableau
Best Suited For
Individuals who enjoy working with data, creating visual insights, and supporting business teams without heavy machine learning or engineering requirements.
Data Scientist
Role Overview
A Data Scientist applies statistics and machine learning to build predictive and analytical models. Their focus is on forecasting outcomes and extracting deeper insights from complex datasets.
Core Skills
- Python or R
- Machine learning
- Probability and statistics
- Data wrangling
- Feature engineering
- Data visualization
Common Tools
Pandas, NumPy, Scikit-learn, Jupyter Notebook, Tableau
Best Suited For
Those interested in mathematics, modeling, and solving complex analytical problems using data.
Business Analyst
Role Overview
A Business Analyst acts as a bridge between stakeholders and technical teams. They define requirements, analyze processes, and ensure that data solutions align with business objectives.
Core Skills
- Business process modeling
- Communication
- Requirements gathering
- Data analysis
- Problem-solving
Common Tools
Excel, Power BI, Tableau, Jira, Confluence
Best Suited For
Professionals who prefer strategic thinking, collaboration, and translating business needs into actionable insights.
Machine Learning Engineer
Role Overview
A Machine Learning Engineer focuses on deploying and maintaining machine learning models in production environments. They ensure scalability, reliability, and performance of AI systems.
Core Skills
- Machine learning
- Data engineering
- ETL and data pipelines
- Software engineering
- MLOps
- Cloud deployment
Common Tools
Python or Java, SQL, Spark, Hadoop, Airflow, MLflow, Docker, Kubernetes
Best Suited For
Engineers who enjoy building robust systems and operationalizing machine learning at scale.
GenAI Engineer
Role Overview
A GenAI Engineer builds applications using large language models and generative AI technologies. Their work includes developing chatbots, AI assistants, and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems.
Core Skills
- Generative AI and LLMs
- Prompt engineering
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
- API integration
- Model evaluation
- Bias mitigation
Common Tools
Transformers, PyTorch, TensorFlow, Hugging Face, LangChain, vector databases
Best Suited For
Those passionate about modern AI innovation and building intelligent, interactive applications.
Key Differences at a Glance
- Data Analysts explain what happened
- Data Scientists predict what will happen
- Business Analysts determine what should happen
- Machine Learning Engineers build how it happens
- GenAI Engineers create AI-driven experiences
Conclusion
Each role in the data and AI ecosystem plays a critical part in transforming data into value. Choosing the right path depends on your interests—whether that is business analysis, statistics, engineering, or cutting-edge artificial intelligence.
Start with foundational skills, gain practical experience, and gradually move toward the role that aligns best with your long-term goals.